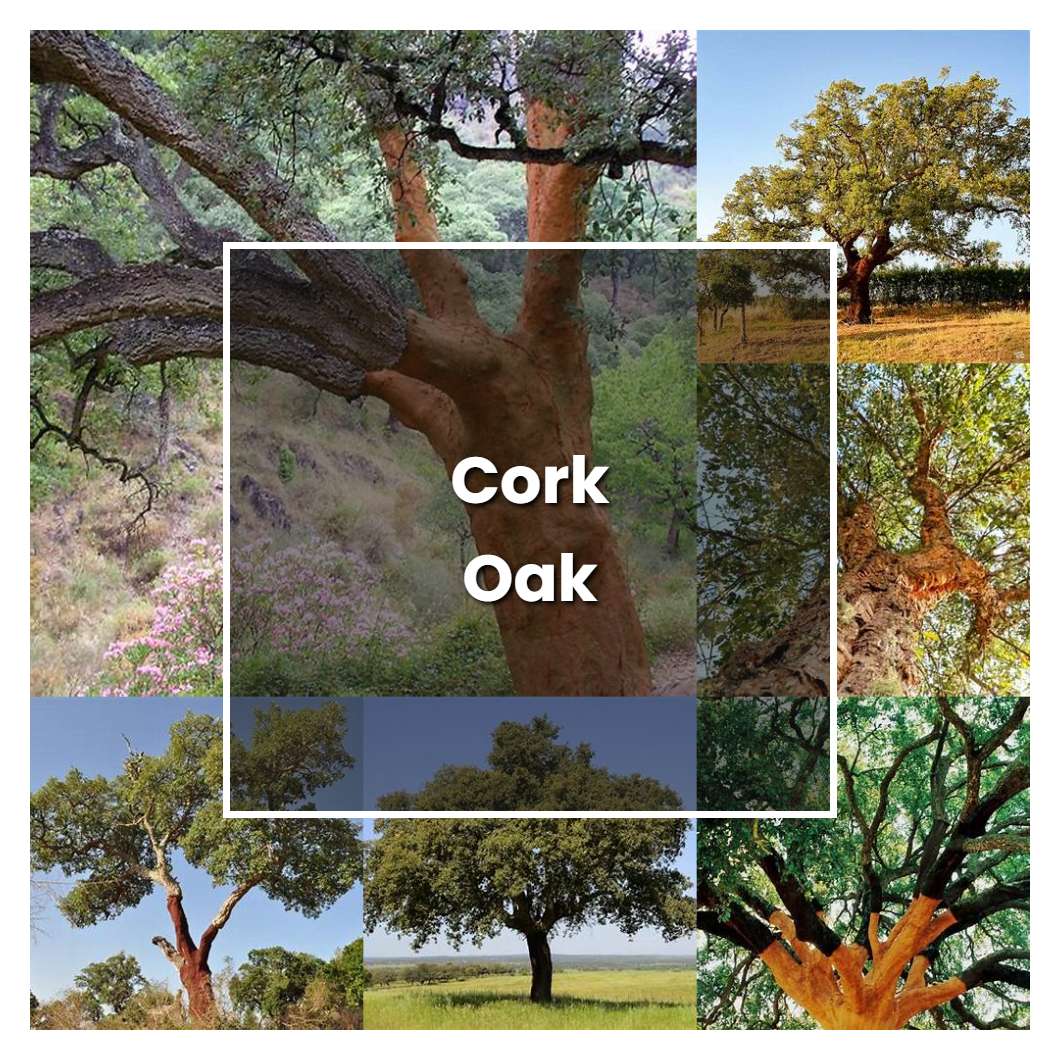
Cork oak is a species of oak native to southwest Europe and northwest Africa. The cork oak is the only tree in the world that can produce cork. Cork is used to make wine stoppers, bulletin boards, and coasters. The cork oak tree has a thick, corky bark that protects it from fire. The cork oak is an evergreen tree and can live to be 200 years old.
Also known as
- Arbutus unedo
- Ceratonia siliqua
- Crataegus monogyna
- Crataegus oxyacantha
- Morus alba
Things to Know
- The Cork Oak is a massive evergreen tree that can grow up to 25m tall.
- It has a wide, round canopy and gnarled, cork-like bark.
- The Cork Oak is native to the Mediterranean region and is widely cultivated in Spain, Portugal, France and Italy.
- The trees are harvested for their valuable cork, which is used to make wine bottle stoppers, corkboard and other products.
- Cork Oak trees can live for up to 200 years and can be harvested every 9 to 12 years.
- The harvesting process is fairly gentle and doesn't harm the tree, as only the outer bark is removed.
- Cork is an excellent insulator and is very fire resistant.
- Cork Oak forests help to prevent soil erosion and provide habitat for many animals.
- The trees are threatened by over-exploitation, forest fires and invasive species.
- Cork Oak forests are protected under European Union law.
Related plant:
Corkscrew Willow
Planting Process
- For cork oak, first step is to find a location that gets full sun and has well-drained soil.
- Next, you need to clear the area of any rocks or debris.
- Once the area is clear, you will need to loosen the soil with a spade or hoe.
- After the soil is loosened, you can then add some compost or manure to help provide nutrients.
- Once the soil is amended, you can then plant your cork oak tree.
- Water the tree regularly, especially during the first growing season.
- Fertilize the tree each spring with a balanced fertilizer.
- Once the tree is established, you can then start to harvest the cork.
- To harvest the cork, you will need to carefully strip it from the tree using a sharp knife.
- After the cork is harvested, you can then use it for various purposes such as wine stoppers or Insulation.
Considering the Soil
About soil condition, cork oak can grow in a variety of soils, but it prefers deep, well-drained, slightly acidic soils. It is tolerant of drought and a wide range of temperatures, from hot summers to cold winters. Cork oak is also tolerant of salt and can be found near the coast.
About light
Like the other trees, the cork oak needs sun to grow. This tree is native to the Mediterranean Basin and can be found in countries like Algeria, Morocco, Portugal, Spain, and Tunisia. The cork oak is an evergreen tree that can live up to 200 years old. This tree can grow up to 20 meters tall and its trunk can be up to 1 meter in diameter. The cork oak is used for the production of cork.
The Temperature
The temperature in the cork oak forest is very warm in the summer and cool in the winter. The average temperature in the summer is about 28 degrees Celsius and in the winter it is about 14 degrees Celsius. The cork oak forest is a great place to visit all year round.
Humidity Aspect
Ideal humidity condition for this plant is around 40% to 60%. The cork oak is a widely adapted species and can withstand a large range of environmental conditions. It is drought tolerant and can survive in relatively dry conditions. It is also tolerant of salt and can withstand salty conditions near the coast.
The Fertilizer
Regarding fertilizer, this family of plant is not too demanding. In fact, they are rather tolerant of poor soils. Cork oaks roots are quite resistant to drought. They have been known to survive temperatures as low as -12 Celsius.
Light requirement
Pruning is an important part of caring for a cork oak tree. Pruning helps the tree to stay healthy and to produce more cork. When pruning a cork oak tree, be sure to remove any dead or diseased branches. Also, prune back any branches that are growing too close to the trunk of the tree.
About Propagating
Propagation of cork oak is most commonly accomplished through rooting of semi-hardwood or hardwood cuttings. Cuttings should be taken from the current year's growth, and be approximately 6-8 inches long. The bottom third of the cutting should be dipped in rooting hormone, and then planted in a well-draining potting mix. Keep the soil moist but not wet, and provide bottom heat if possible. After a few weeks, the cuttings should develop roots and can be transplanted into their permanent location.
Growth Rate
Usually, the plant growth rate studies have been done in Portugal, Spain, and Morocco. In Portugal, the mean annual increase of cork oak trees is about 1.2 m3/ha. In Spain, the average cork oak growth rate is 1.4 m3/ha/year. In Morocco, the cork oak growth rate is about 2.5 m3/ha/year.
Common Problems
Common problems for this kind of plant trees are quite a few. They include pests and diseases, such as the scale insect, which can cause the tree to produce less cork. In addition, cork oaks are susceptible to wind and water damage, which can lead to the tree falling over.
Growing Tips
- Make sure to plant your cork oak in an area that receives full sun.
- Cork oaks need well-drained soil in order to thrive.
- Be sure to water your cork oak regularly, especially during the hotter months.
- Fertilize your cork oak every few months to help it remain healthy and vigorous.
- Prune your cork oak regularly to encourage new growth and maintain its shape.
- Protect your cork oak from extreme weather conditions, such as strong winds and cold temperatures.
- Keep an eye out for pests and diseases that could affect your cork oak.
- Harvesting cork from your cork oak is relatively easy and can be done every few years.
- If you plan on replanting your cork oak, make sure to do so during the cooler months.
- Cork oaks can live for hundreds of years, so
You May Like
- Quercus cerris: The cork oak is a very hardy and long-lived deciduous tree found across southern Europe. It is also known as the Italian oak, Turkish oak and Lugano oak.
- Quercus robur: The common oak is a large deciduous tree found across Europe. It is also known as the English oak and the pedunculate oak.
- Quercus suber: The cork oak is a deciduous tree native to the Mediterranean region. It is also known as the Algerian oak and the Moroccan oak.
- Quercus ilex: The evergreen oak is a large tree found across the Mediterranean region. It is also known as the holly oak and the holm oak.
- Quercus pubescens: The downy oak is a deciduous tree found in Europe and North Africa. It is also known as the French oak
Source:
Quercus variabilis (Chinese Cork Oak, Oaks, Oriental Oak)
Quercus suber, cork oak | Trees of Stanford & Environs
The rationale behind cork properties: A review of structure and ...
Reviewed & Published by Richelle
Submitted by our contributor

